
Next, it filters that output through grep, using a filter that matches an uppercase G followed by a tab character. The overall effect is that the second form produces one line of du output for each file and folder contained immediately inside the user's home folder, and doesn't descend into subfolders to produce detailed usage output for their subfolders. The other du options that the second form includes and the first doesn't are x, which makes du ignore filesystems on secondary devices like USB sticks that might have been mounted on folders inside the ones it's looking at, and s, which makes it not report explicitly on the sizes of folders inside those it's being specifically asked about, instead producing only a summary usage number for each such folder. Note that the typical software-enginerd insistence on misusing SI unit symbols to denote IEC binary multiples means that the numbers are not particularly human-meaningful, especially for the larger units. The second form uses the alternative h (for "human-readable") option, which makes the numbers appear with a B, K, M, G, T or P suffix for bytes, kibibytes, mebibytes, gibibytes, tebibytes and pebibytes respectively. The k option passed to du in the first form makes all the disk usage numbers appear as a pure number based on a consistent size unit, the kibibyte (1024 bytes).

For folders, the amount of disk space used includes that used by all files and folders inside the folder as well as by the folder itself. Each output line consists of a number representing the amount of disk space actually used by the file, then a tab character, then the pathname of the file, then a newline. Not sure why the second form would need to do that, since everything inside /Users/yourusername/ would normally be completely readable to the yourusername account even without sudo's help.ĭu produces one line of text output for each file or folder it reports on. The first form does this so that du will be able to see inside folders owned by the system or other user accounts, in order not to miss anything. However, the first form runs it against the root of the entire Unix file hierarchy, named /, while the second runs it against a list consisting of all files and folders immediately contained within the user's own home folder.īoth forms use sudo to make du run with administrative privileges rather than those of the user account whose Terminal it's launched from. Sudo du -shx /Users/yourusernamehere/* | grep $'G\t' | sort -rn | head -n 10īoth forms rely on the du command to generate the disk usage information we're interested in. When you're doing this kind of work, simple and slow and thorough is good fancy and fast and assumption-making, not so much.įor those still following along at home, the similarities and differences between It would not have found core dumps in /cores, for example. Posted by flabdablet at 1:02 PM on Novemīest answer: That's essentially the same solution as I already recommended, only fancier and faster and therefore more likely to miss stuff. Never did trust those fancy newfangled GUI tools for this class of inquiry.
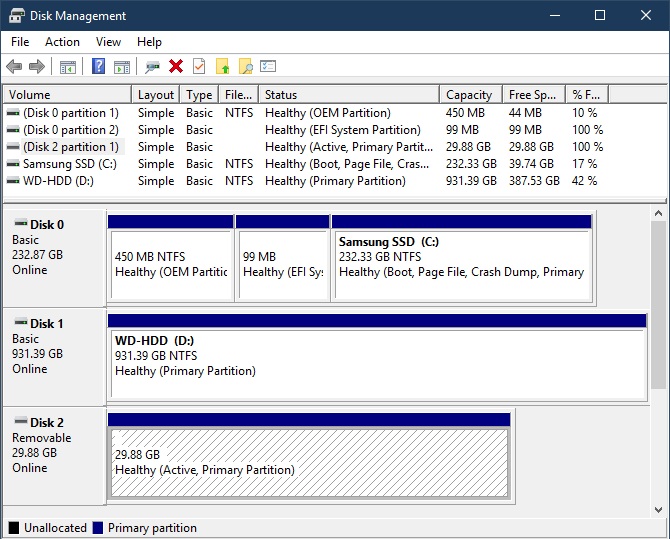
This should show you actual amounts of space used on each in-use filesystem, and you should be able to match those up with the amounts that du showed you for some of the larger folders. Next, back in the Terminal window, type df and press Enter. You should see a list of every directory (folder) on your whole system, each one prefixed by a number showing the disk usage of all the files it contains in KiB (1024-byte) units, with the biggest ones sorted to the top. Once that's happened, find the system /tmp folder in the Finder and open report.txt with Textedit. Type it in and press Enter it won't echo anything at all for each character you type.Īfter entering the password, du will rattle your hard disk while appearing to do nothing for some time before the next command prompt appears. Sudo will first ask for your admin password. Best answer: Try opening a Terminal window and pasting in the following command line:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
